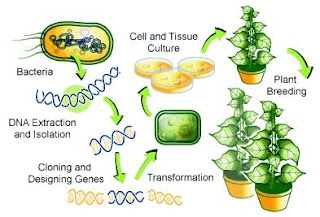
 “Transgenic recombinant plants” are created in a laboratory by adding at least one gene to the plants genome. The technique used to do this is often known as “Transformation”.
“Transgenic recombinant plants” are created in a laboratory by adding at least one gene to the plants genome. The technique used to do this is often known as “Transformation”.There are several ways to do this –
• You can infect the plant cells with small molecules of DNA acting as carriers of the modified gene.
• Shoot the gene directly into the cell and hope it succeeds.
Usually the same benefits apply as genetic modification; combinations of improved nutritional values, increased resistances to pesticides, salts, herbicides and diseases
However, there are (again) several difficulties in transgenic plants. These include genes for herbicide resistance (like in corn) somehow transferring into a weed species, making the weeds much harder to manage, or toxic genes transferring into the pollen of a plant may endanger pollinators, like honey bees. Even though there are problems, farmers are embracing transgenic crops, as there were 100,000,000hA of transgenic crops planted in ‘06
No comments:
Post a Comment